ECG quiz: What do these traces of palpitations indicate?
Question 1
What abnormalities are present on this ECG?
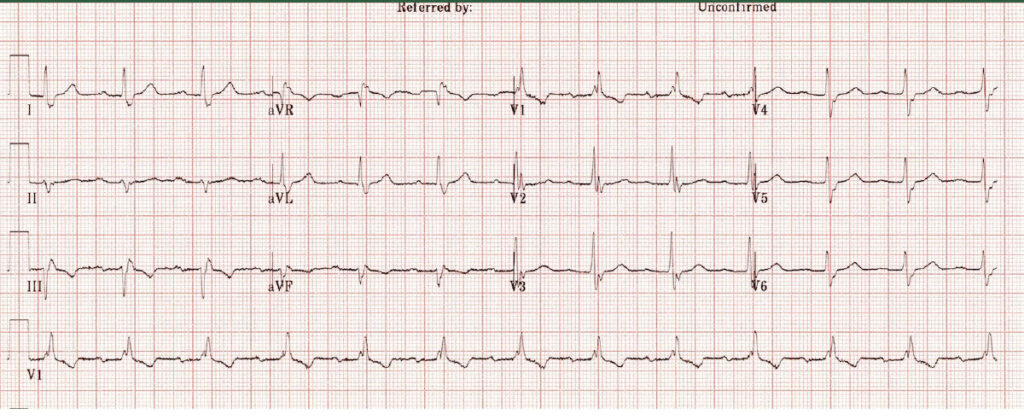
A There is LBBB
B There is RBBB and second degree heart block
C There is RBBB
D There is RBBB, first degree heart block and left axis deviation
E There is LBBB and first degree heart block
Answer Right bundle branch block
Explanation
There is a broad QRS complex which is predominantly positive in V1 indicating RBBB.
The PR interval is > 200ms or 1 big square indicating first degree heart block
The QRS complex is positive in lead I and negative in lead II and also negative in lead aVF – indicating left axis deviation
TIP When you see RBBB always look for 1st degree heart block and/or left axis deviation as this indicates much extensive conductive tissue damage – in this case trifascicular block which is high risk for developing complete heart block
Question 2
A 29 year old man presents with fast palpitations playing football. Which of the following is true?
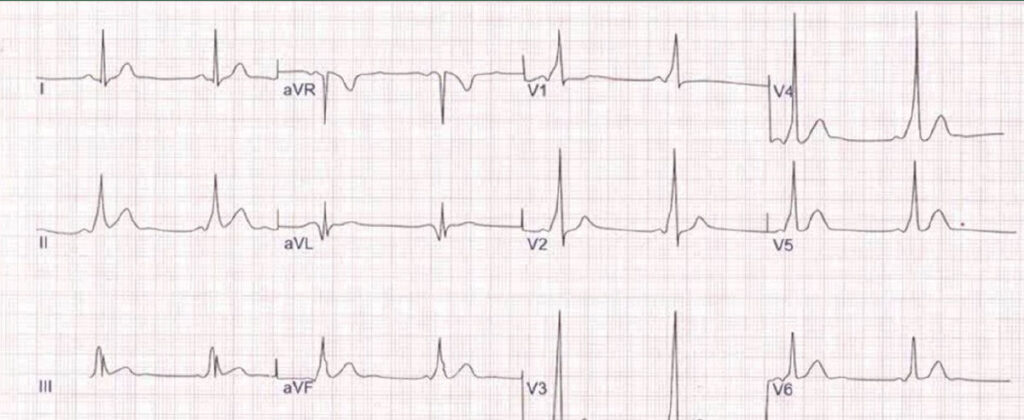
A The ECG is normal and he should be reassured
B The ECG is normal but he should have an open access 24hr ECG
C The ECG is normal and he should be given a beta blocker for symptomatic relief
D The ECG is abnormal and he should be referred to Cardiology
E The ECG has minor abnormalities and he should have an open access echo and 24hr ECG
Answer The ECG is abnormal and he should be referred to Cardiology
Explanation
The PR interval is very short indicating a bypass of the AV node via an accessory pathway. The QRS complexes also look abnormal with an initial shouldering of the complexes known as a delta waves. This reflects the earlier ventricular depolarization via the accessory pathway.
This patient has a good substrate for developing re-entrant tachycardias and SVTs ie electrical activity going down the AV node but then back up the accessory pathway rapidly cycling.
These patients should be referred to an EP cardiologist for discussion of catheter ablation of the accessory pathway which has a very high cure rate.
TIP In any young patient with suspected episodes of SVT, the PR interval should be documented as should the presence or not of delta waves.
Question 3
A young man presents with palpitations. What does his ECG show?
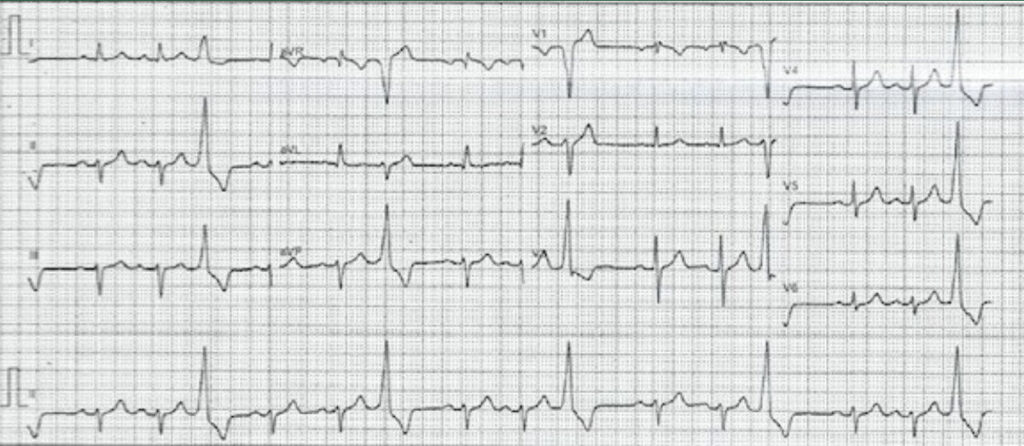
A Atrial ectopics
B Ventricular bigeminy pattern of ectopics
C Ventricular trigeminy pattern of ectopics
D Ventricular triplets
E Ventricular trigeminy pattern of ectopics
Answer Ventricular trigeminy pattern of ectopics
Explanation
There are clearly extra QRS complexes that are of different morphology compared to the QRS complexes with preceding p waves ie the sinus beats. The extra QRS complexes are broader and bigger indicating ventricular ectopics. They occur after every 2nd sinus beat which is called trigeminy.
TIP Have a low threshold for requesting a 24 hour holter in patients with frequent ventricular ectopics to gauge the ventricular ectopic burden. If the 24 hour holter shows > 10000 ectopic beats or > 10% ectopic burden then an echocardiogram and cardiology referral is merited.
Pulse July survey
Take our July 2025 survey to potentially win £1.000 worth of tokens

Visit Pulse Reference for details on 140 symptoms, including easily searchable symptoms and categories, offering you a free platform to check symptoms and receive potential diagnoses during consultations.










