As part of a new series on Pulse, Dr Yassir Javaid, a GPwSI in cardiology and echocardiography, asks what these ECGs could signify. See bottom of the page for answers
Question 1
A 70-year-old woman presents to A&E with sudden onset breathlessness. She also notices a fast heart beat and has a history of thyrotoxicosis and previous TIA. What is her rhythm?
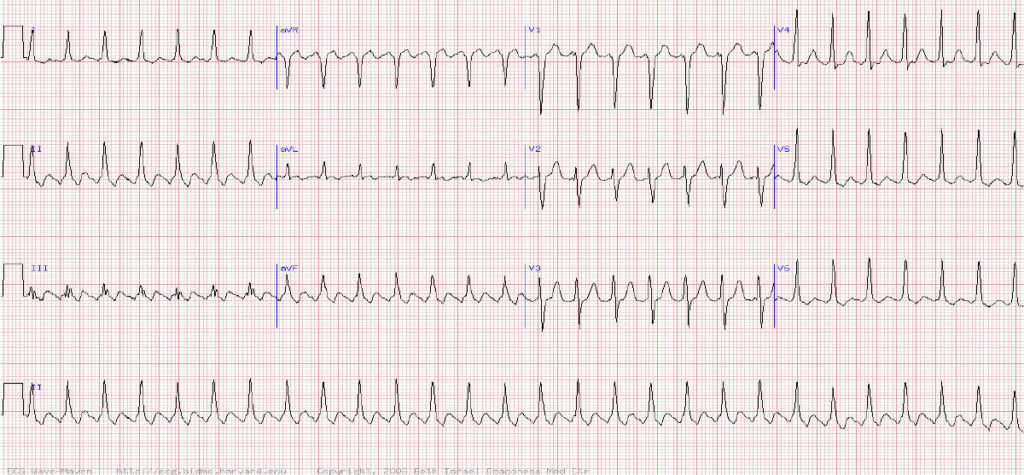
A Sinus tachycardia
B Atrial tachycardia
C AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT)
D Atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction
E Atrial fibrillation
Question 2
This 78-year-old man presents with lightheaded episodes. What does his ECG show?
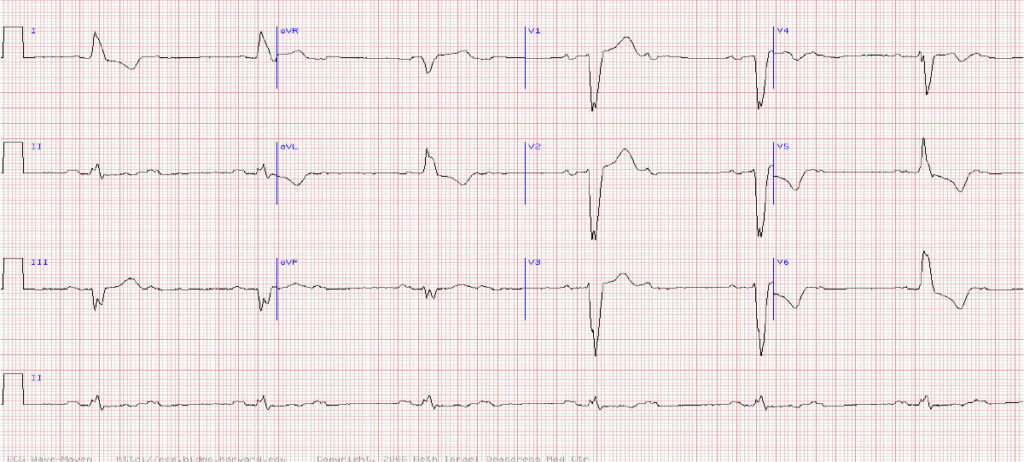
A Sinus bradycardia with left bundle branch block (LBBB)
B Sinus rhythm with 2:1 AV block and LBBB
C Sinus rhythm with complete (third degree) AV heart block
D Atrial tachycardia with block
E Idioventricular escape rhythm
Question 3
21-year-old female seen in A&E with complaints of chest pain and shortness of breath. What does this ECG show?
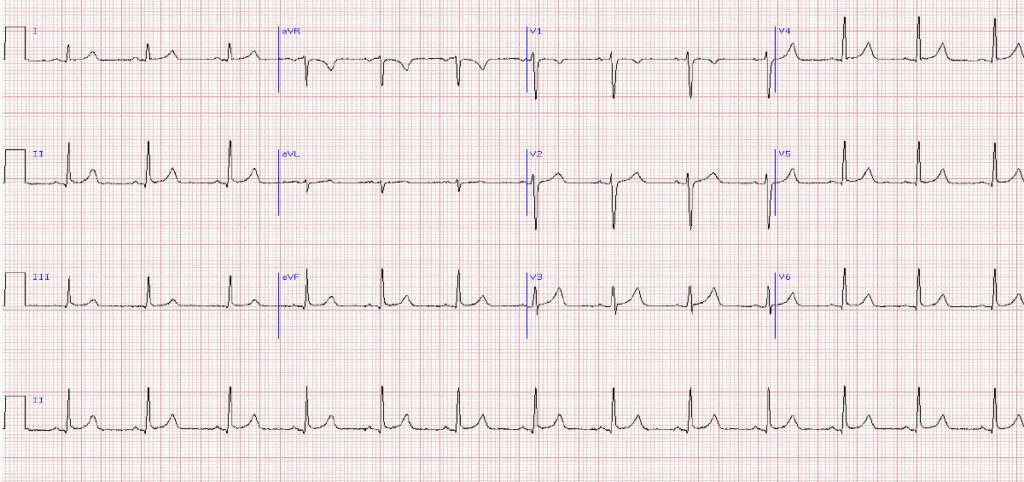
A Right atrial abnormality
B Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH)
C Left atrial abnormality (LAA)
D No abnormality
E Right ventricular hypertrophy
Answers
Question 1 Atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction
Explanation
There is clearly a tachycardia with narrow QRS complexes indicating a supraventricular rhythm.
The clues to the aetiology are the heart rate of almost exactly 150 / min and the saw tooth waves seen best in the inferior leads of II, III and aVF.
TIP Think atrial flutter for any narrow complex tachycardia of around 150bpm. In atrial flutter there is a regular atrial rate of 300bpm which is too high for the AV node to conduct. The AV node therefore often conducts every other atrial flutter wave resulting in a QRS rate of 150bpm.
Question 2 Sinus rhythm with 2:1 AV block and LBBB
Explanation
Any elderly patient with syncope or presyncope should have a prompt ECG to rule out high degree heart block.
TIP Regular p waves indicate the rhythm is sinus. However, every other p wave is not followed by a QRS compelx indicating a high degree heart block – in this case 2:1 block (2nd degree Mobitz type 2). This requires urgent referral for a pacemaker (discuss with on call medical team).
In addition there is also a broad QRS complex with a QRS complex in V1 that is predominantly negative indicating a LBBB.
Answer No abnormality
Explanation
There are no significant abnormalities on this ECG.
TIP A good quick preliminary screen of an ECG should involve rate, rhythm and axis – in this ECG the rate is around 75bpm, the rhythm is sinus (there are regular p waves and every p wave is followed by a QRS indicating sinus rhythm with no high degree heart block) and the QRS complexes in both leads I and II are both positive (indicating a normal cardiac axis).
Pulse October survey
Take our July 2025 survey to potentially win £1.000 worth of tokens













